The Basics: CT Scanning
The basics of CT scanning technology, and how it can help your next project
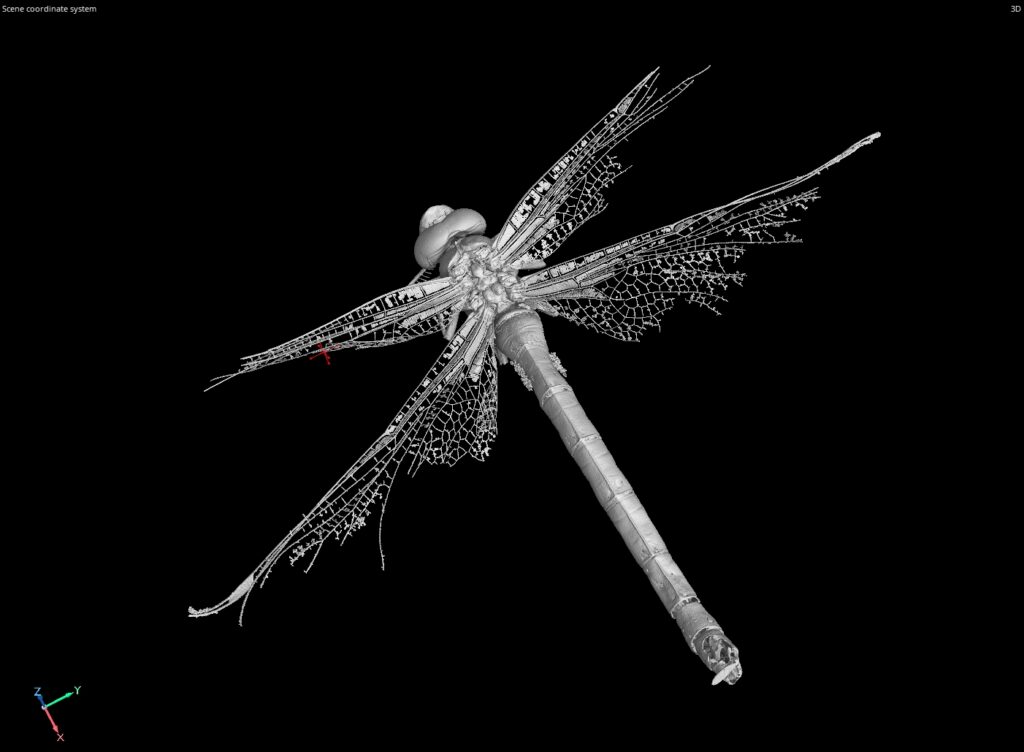
Computed Tomography (CT) scanning is a medical imaging technique that has proven to be an invaluable tool for detecting and diagnosing various medical conditions. However, CT scanning is not limited to medical applications and has increasingly found use in the manufacturing industry as well. CT scanning provides a non-destructive way to inspect and analyse the internal structures of objects, making it an important tool for quality control and product development.
CT scanning works by using X-rays to produce a series of 2D images or “slices” of an object. These slices are then digitally reconstructed into a 3D image of the object’s internal structure. CT scanning can provide a detailed view of an object’s internal features, such as its density, shape, and size. This level of detail allows for the detection of defects or anomalies that might not be visible from the outside.
So what Can It Be Used For?
One of the primary applications of CT scanning in manufacturing is quality control. CT scanning can be used to inspect and analyse the internal structures of manufactured components, such as engine parts, electronics, and other complex assemblies. By using CT scanning, manufacturers can quickly detect defects or anomalies that might not be visible from the outside, allowing them to adjust their manufacturing process to improve the quality of their products.
CT scanning can also be used in product development. By providing a detailed view of an object’s internal structure, CT scanning can help manufacturers optimize their product designs. For example, CT scanning can be used to analyse the internal structures of components, such as turbine blades or engine blocks, to identify areas that are prone to stress or other types of wear and tear. This information can then be used to make design modifications that will improve the durability and performance of the product.
Combining With Other Technologies
In addition to quality control and product development, CT scanning can also be used in reverse engineering. Reverse engineering involves taking an existing object and creating a 3D model of it. CT scanning can provide a detailed view of an object’s internal structure, which can then be used to create an accurate 3D model. This can be particularly useful in industries such as aerospace, where it is necessary to analyse and replicate components of existing aircraft and spacecraft. If you want to find out about reverse engineering in more detail, we also have a Basics article about it here: (insert link here)
Another application of CT scanning in manufacturing is in the inspection of additive manufacturing (AM) parts. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a process where components are built layer by layer using materials such as metal, plastic, or ceramic. CT scanning can be used to inspect the internal structure of AM parts to ensure that they have been manufactured to the required specifications. This can help to reduce the risk of defects and improve the overall quality of the parts.
In Conclusion
CT scanning has helped revolutionise and streamline manufacturing in a way that never could have been predicted just a few decades ago. If CT scanning could improve your manufacturing, get in touch with OR3D at:
Phone – 01691 777774
email – info@or3d.co.uk
Our Contact page – https://www.or3d.co.uk/contact-us/